Navigating Alzheimer's Treatment: Current Strategies and Hopeful Advances
Alzheimer's disease a progressive neurodegenerative disorder is the most common cause of dementia among older adults. While there is no cure for Alzheimer's there are treatments available that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. This blog explores the current landscape of Alzheimer's treatment including medications therapies and emerging research that offers hope for the future.
1. Medications for Alzheimer's:
Cholinesterase Inhibitors (Donepezil Rivastigmine Galantamine): These drugs work by boosting levels of a chemical messenger involved in memory and judgment. They are mainly used for mild to moderate Alzheimer's.
Memantine (Namenda): Used to treat moderate to severe Alzheimer's this medication works by regulating the activity of glutamate a chemical involved in information processing storage and retrieval.
Combination Therapy (Namzaric): A combination of memantine and donepezil this is used for moderate to severe Alzheimer's cases.
2. Managing Behavioral Symptoms:
Antidepressants: To help with the depression and irritability that can accompany Alzheimer's.
Anxiolytics: Used cautiously to reduce anxiety.
Antipsychotic Medications: Sometimes prescribed for symptoms like aggression agitation and hallucinations.
3. Supportive Therapies and Care:
Cognitive Stimulation Therapy: Activities and exercises to stimulate thinking concentration and memory.
Occupational Therapy: Helps with coping strategies for daily tasks and improving home safety to prevent accidents.
Physical Activity and Exercise: Regular exercise can help maintain muscle strength mobility and overall health.
4. Lifestyle and Home Remedies:
Healthy Diet: Diets like the Mediterranean diet rich in fruits vegetables whole grains and lean proteins may help protect brain health.
Social Engagement: Staying socially active can help preserve mental function.
Mental Stimulation: Activities like puzzles reading and games can help keep the mind engaged.
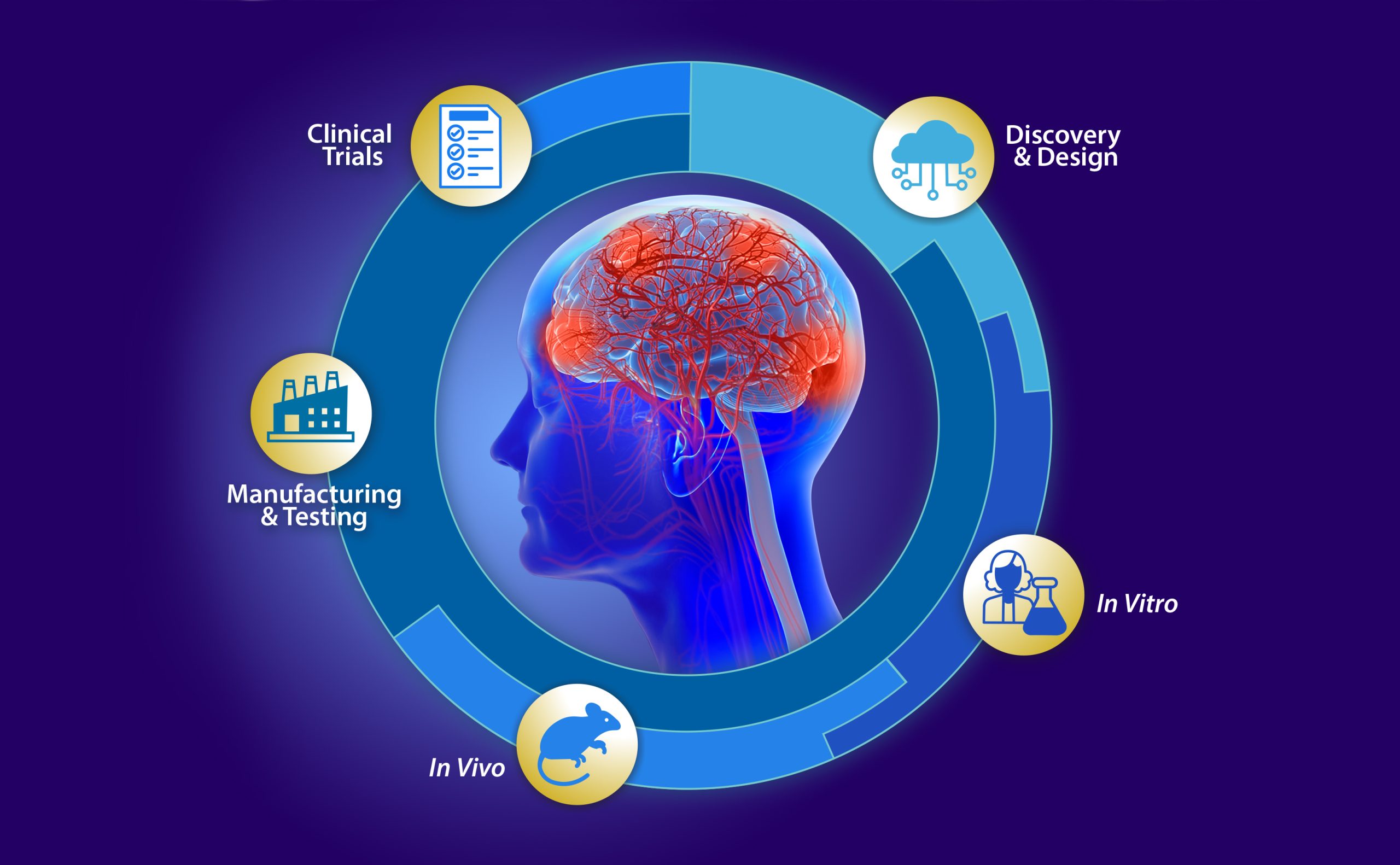
5. Emerging Research and Future Treatments:
Clinical Trials: Ongoing research is exploring new medications and treatments. Participation in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments.
Gene Therapy and Stem Cell Research: These areas hold promise for future breakthroughs in Alzheimer's treatment.
Conclusion: While Alzheimer's disease presents significant challenges there are treatments and strategies that can help manage its symptoms and improve quality of life. Ongoing research continues to bring hope with the potential for new and more effective treatments on the horizon.